Services We Offer
Elbow
The elbow may look like a simple hinge, but it’s actually a complex joint that allows you to bend, straighten, rotate, and stabilize your forearm. Because the elbow works in close connection with the shoulder, wrist, and hand, pain in this area often affects daily tasks like lifting, gripping, or even typing.
Anatomy of the Elbow
The elbow is formed where three bones meet: the humerus (upper arm bone), the ulna, and the radius (forearm bones). These are supported by cartilage, ligaments, and muscles that guide both bending and rotation. The main movements of the elbow are flexion and extension, but the joint also allows the forearm to turn palm up (supination) and palm down (pronation). Surrounding muscles — including the biceps, triceps, forearm flexors, and extensors — all play an important role in controlling this motion and keeping the joint stable.
Balancing Movement and Stability
The elbow must strike a delicate balance between being mobile enough for precise movements and strong enough to handle the forces placed on it during pushing, pulling, and gripping. Unlike the shoulder, the elbow sacrifices some range of motion in exchange for greater stability. When this balance is disrupted through overuse, injury, or poor mechanics, pain and dysfunction quickly follow.
Problems arise when this balance is disrupted. Too much mobility without control can cause strain and instability, while excessive stiffness can limit movement and increase stress on other joints like the hips or knees.
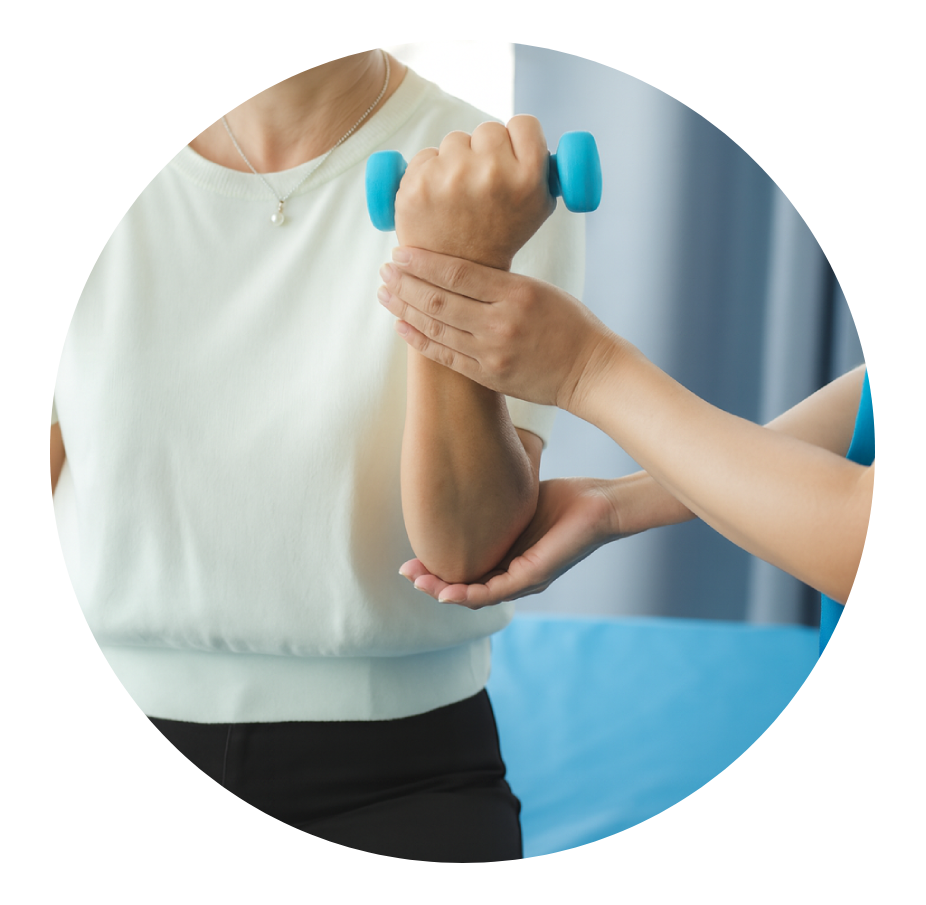


Common Causes of Elbow Pain
Elbow pain is frequently linked to repetitive stress, trauma, or sports-related movements. Overuse from work tasks or athletic activities can strain the tendons and muscles that cross the joint.

Typical causes include:

Tennis elbow (lateral epicondylitis)

Golfer’s elbow (medial epicondylitis)

Elbow bursitis (olecranon bursitis)

Ulnar nerve entrapment (cubital tunnel syndrome)

Ligament sprains or tears

Arthritis

Fractures or dislocations

Overuse from repetitive lifting or gripping

Common symptoms include:

Sharp or aching pain

Tenderness over the bony parts of the elbow

Weakness in grip strength

Stiffness when bending or straightening

Tingling or numbness down the forearm

Swelling around the joint
How Physical Therapy Helps You
Elbow pain can interfere with simple daily tasks like holding a coffee cup, carrying groceries, or using a computer mouse — not just sports or heavy lifting. A physical therapist will first evaluate your range of motion, muscle strength, posture, and movement mechanics to pinpoint the cause of your pain.
Treatment often combines hands-on techniques to reduce irritation, specific exercises to strengthen the forearm and shoulder muscles, and ergonomic education to modify the way you perform repetitive tasks. The goal is not only to relieve pain but also to restore normal function and prevent recurrence.
With the right approach, you can regain pain-free movement and return to the activities you enjoy.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is tennis elbow and how is it treated?
Tennis elbow is irritation of the tendons on the outside of the elbow, usually from repetitive gripping or lifting. Physical therapy focuses on reducing irritation and strengthening the forearm to restore normal function.
Can elbow pain be caused by the neck or shoulder?
Yes. Because nerves and muscles run through multiple regions, pain felt in the elbow can sometimes originate from the neck, shoulder, or even the wrist. A thorough evaluation helps identify the true source.
Do I need to stop all activities if my elbow hurts?
Not usually. Complete rest may weaken the muscles further. Guided modifications and corrective exercises from a therapist are more effective for recovery.
How long does it take for elbow pain to improve?
Minor strains may resolve in a few weeks with therapy, while chronic tendon irritation can take several months of consistent care to fully heal.
Can physical therapy help if I’ve had elbow surgery?
Absolutely. Post-surgical rehabilitation is often critical for regaining range of motion, strength, and preventing stiffness after procedures like ligament repair or fracture surgery.

