Services We Offer
Ankle & Foot
The ankle and foot are often discussed together as one joint complex because of their close interaction. Their coordinated structure allows for stability and balance, even when standing on uneven or moving surfaces such as a boat.
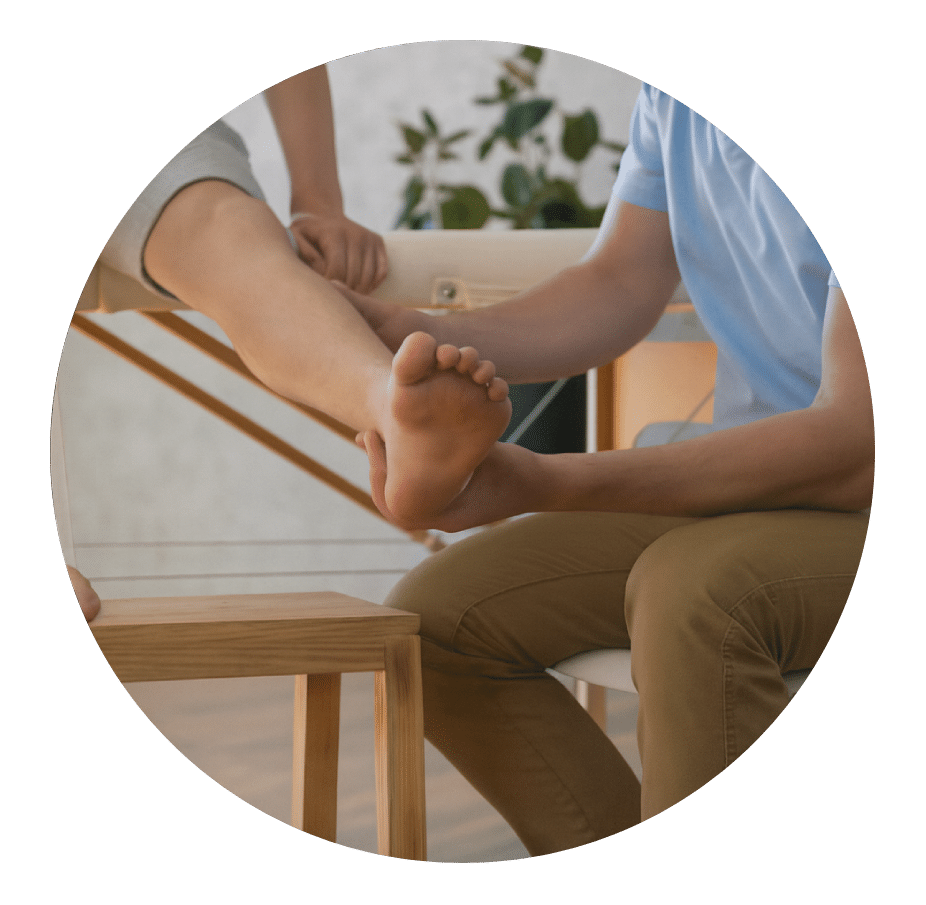
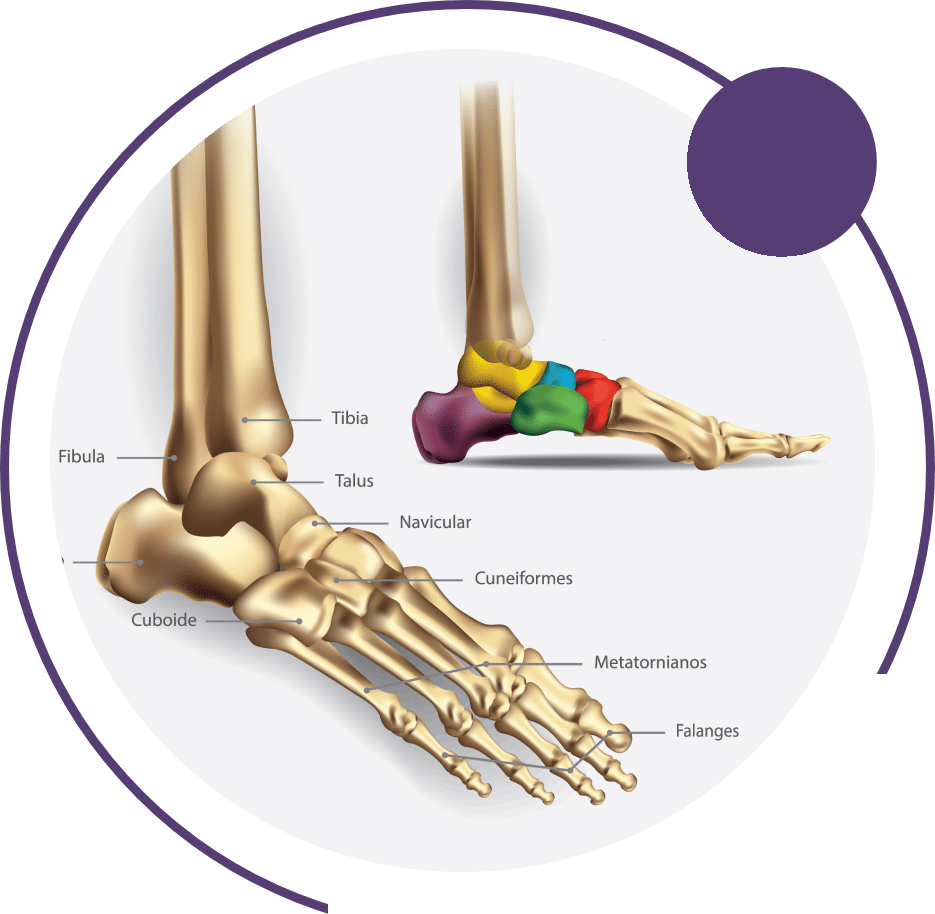

Ankle Joints
Full ankle range of motion comes from three interconnected joints: the tibiofibular joint, the talocrural joint, and the subtalar joint. These joints work together to support upright posture and smooth movement.
Regions of the Foot
The foot can be divided into three regions: the hindfoot, midfoot, and forefoot. The hindfoot connects to the midfoot through the midtarsal joint, while the midfoot connects to the forefoot through the tarsometatarsal joint complex.
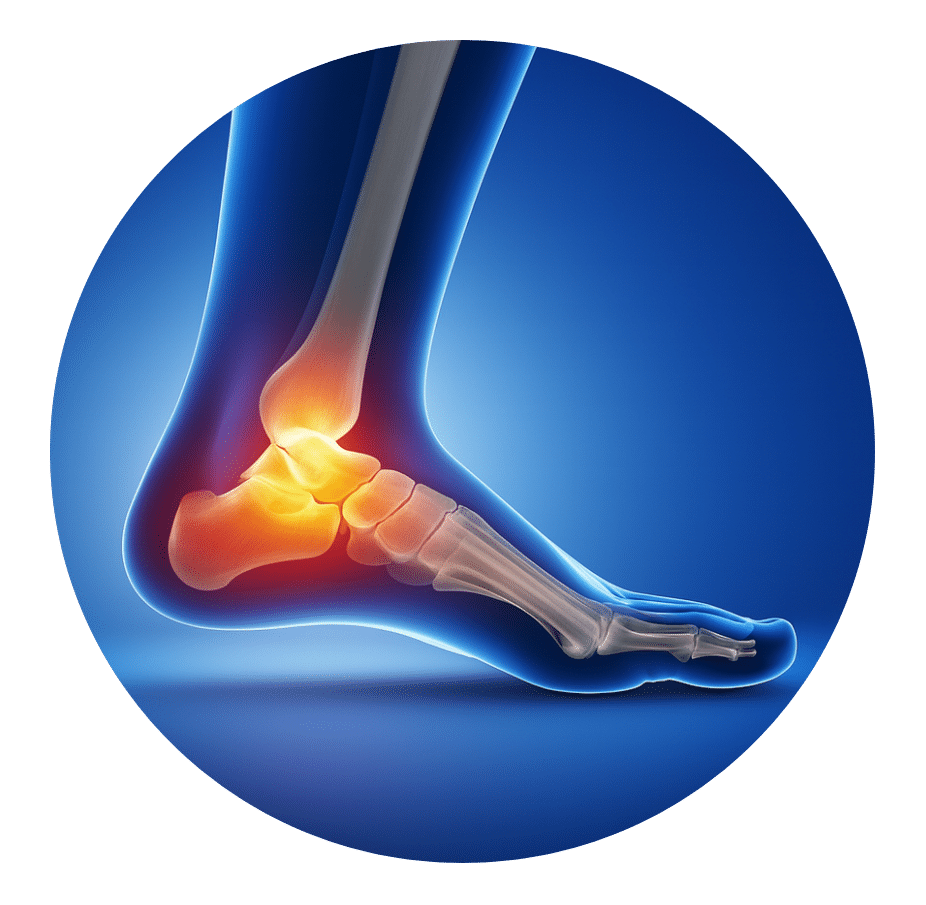

Movements and Clinical Importance
Movements of the ankle and foot include plantar flexion, dorsiflexion, inversion, and eversion. These can also combine into pronation and supination, which are essential for walking and adapting to different surfaces. Because of the complexity and the many interconnected joints and structures involved, the ankle and foot are especially prone to injuries. Their proper function is crucial for maintaining mobility, balance, and performing everyday activities.
Common Causes Of Ankle And Foot Pain
Ankle and foot pain can be unexpected like randomly waking up with heel pain or following a traumatic event. Prolonged standing and walking are common causes of pain, but the severity can vary depending on your day-to-day activities.

Other causes of ankle pain include:

Anterior ankle impingement syndrome

Ankle sprains such as a “rolled ankle”

Achilles tendinopathy

Syndesmotic sprain

Sinus tarsi syndrome

Tarsal tunnel syndrome

Other types of tendonitis

Other ligament sprains or tears

Muscle strains or tears

Fractures

And more

Other causes of foot pain include:

Plantar fasciitis

Metatarsalgia

Morton’s neuroma

Turf toe

Lisfranc fracture

Ligament sprains or tears

Muscle strains or tears

Fractures

And more

Common symptoms include:

Difficulty walking

Clicking/popping

Swelling or stiffness

Pain (aching, sharp, dull)

Difficulty moving bending ankle and toes
How Physical Therapy Helps You
Many issues occur in ankles and feet because most activities require us to be on our feet. Your symptoms can be local (within the ankle/foot), referred pain from a muscle, or radiating from the spine. A physical therapist can evaluate you to determine the cause of your symptoms to help manage pain, improve mobility, and restore strength.
Following the initial evaluation, your physical therapist will determine and discuss the cause of your pain or issues. Together, you and your physical therapist will set goals specific to your needs and create a plan of care. Your plan of care will help you accomplish your goals and get you back to what you enjoy doing!
Living with pain does not have to be your new norm. Contact us to get a free phone consult and schedule an initial appointment if you’re suffering from ankle and/or foot pain.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why are the ankle and foot considered one joint complex?
Because the ankle and foot work together to provide balance, stability, and mobility, they are often discussed as a single functional unit in clinical settings.
Which joints make up the ankle?
The ankle’s range of motion comes from three main joints: the tibiofibular joint, the talocrural joint, and the subtalar joint. Together, they allow smooth and controlled movement.
How is the foot divided?
The foot has three regions: the hindfoot, midfoot, and forefoot. The midtarsal joint connects the hindfoot to the midfoot, while the tarsometatarsal joint complex links the midfoot to the forefoot.
What movements can the ankle and foot perform?
They can move in single directions—plantar flexion, dorsiflexion, inversion, and eversion—or combine these into pronation and supination, which are vital for walking and adapting to uneven surfaces.
Why are ankle and foot injuries so common?
Due to the large number of interconnected joints and structures, this area is complex and bears constant load during daily activities. As a result, it is prone to overuse, sprains, and other injuries.

